Data Processing
Batch Process
Kretz recommend to start from batch processing and move to streaming if needed 1.
Stream Process
Three methods to stream data
- At Least Once:
- message gets processed once or multiple times never dropped
- e.g., time-based GPS data in fleet management, if the stream data has the same timestamp, then we just override the existing data, we do not care how many times the data is being processed or streamed.
- At Most Once:
- okay to drop a message
- only processed once at max
- e.g. accident events, do not record multiple times otherwise it is gonna be a misleading signal that the accident happens a lot.
- Exactly Once:
- do not drop message
- e.g., banking
Tools
Spark
[[Spark]] Data Processing - (Py)Spark Processing Data using (Py)Spark is in-memory storage.
- e.g., Load from HDFS to memory of workers,
- input data and intermediate results are in memory, no disk writes,
- no clear map-reduce stage anymore,
- can be complex analysis,
- supports streaming analysis,
- native support for scheduling jobs.
This figure is a screenshot from the book by Adreas Kretz.
RDD
Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD) is the core of Spark. It is a good tool to work on low level optimizations2.
- Similar to Map-Reduce
- Lower level
- Old stuff
- Now dataframes/datasets
DataFrames and Datasets
DataFrames and Datasets share the same API since Apache Spark 2.02. They are easier to use than RDD.
Datasets are typed. In this way we can catch more errors in compile time.
SparkSQL
SparkSQL is used to access dataframes.
Run Complex Models in Spark
One could run complex machine learning models directly on Spark using tools such as Tensorflow and MLlib.
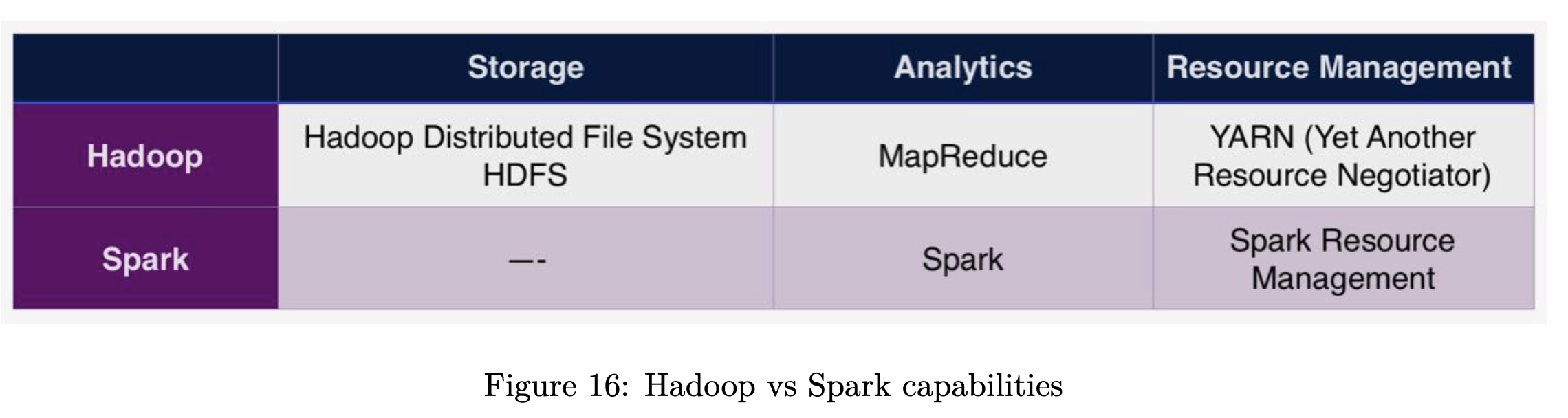
Resource management
Spark has its own resource management module. But one could also use Hadoop’s YARN.
When to use Spark
If the processing is simple (summing, counting, etc): Map-reduce is good enough
If the analytics is complex (ML) or need speed: Spark
Spark + Hadoop
e.g, use YARN to manage physical resources.
If Spark and Hadoop is running on the same workers, doesn’t make sense to have multiple resource managers. In this case, use Hadoop’s YARN.
Use Data from Hadoop
Use the local Hadoop data in Spark
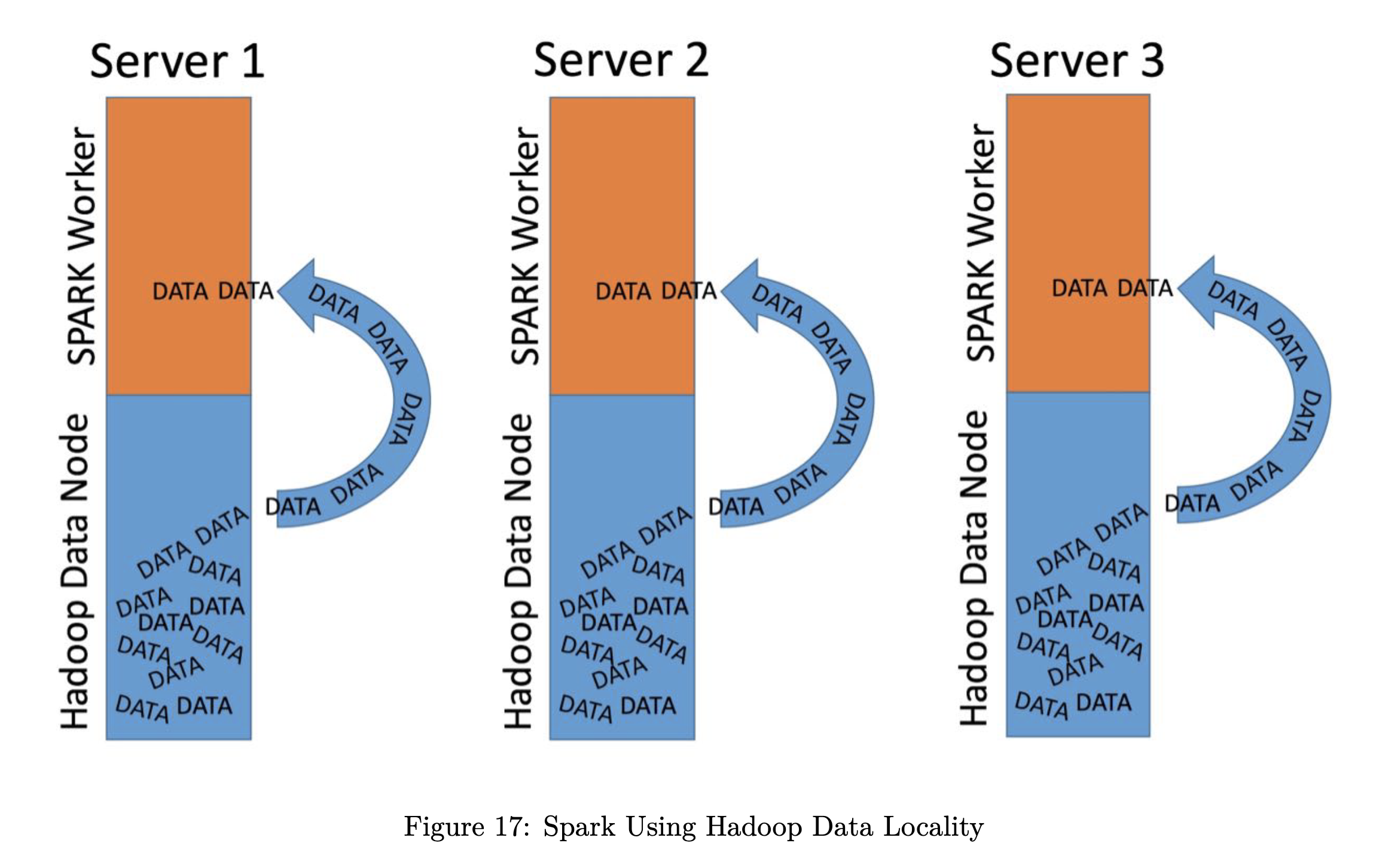
This figure is a screenshot from the book by Adreas Kretz.
Flink
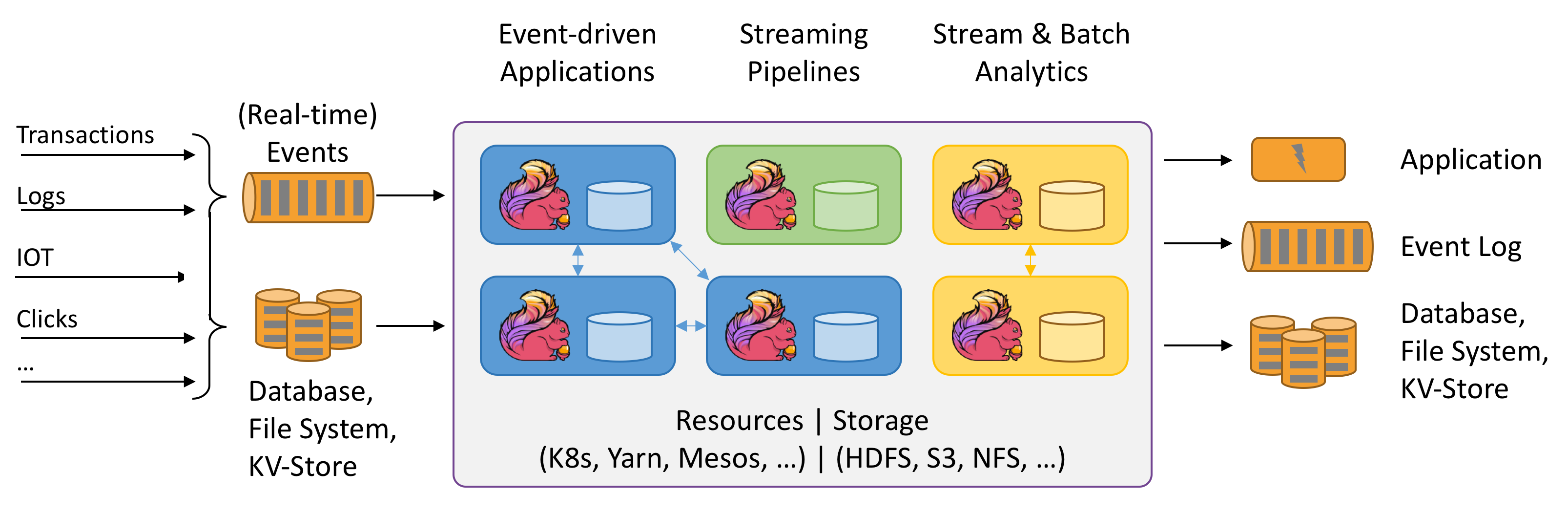
From the website of Apache Flink
- Stateful Computations
- Event-driven applications
- Stream and Batch analysis
- ETL
- Kretz2019 The Data Engineering Cookbook
- databricksblog2016 Damji JJD. A Tale of Three Apache Spark APIs: RDDs vs DataFrames and Datasets. In: Databricks [Internet]. 14 Jul 2016 [cited 1 Feb 2022]. Available: https://databricks.com/blog/2016/07/14/a-tale-of-three-apache-spark-apis-rdds-dataframes-and-datasets.html
wiki/data-engeering-for-data-scientist/data-processing:wiki/data-engeering-for-data-scientist/data-processing Links to:L Ma (2021). 'Data Processing', Datumorphism, 05 April. Available at: https://datumorphism.leima.is/wiki/data-engeering-for-data-scientist/data-processing/.